Multiple sclerosis patient-derived spontaneous B cells have distinct EBV and host gene expression profiles in active disease – Nature Microbiology
Introduction: In this groundbreaking study, researchers have uncovered unique gene expression profiles in B cells derived from patients with multiple sclerosis during active disease. The findings shed new light on the role of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and host genes in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis.
What are the gene expression profiles of B cells in multiple sclerosis patients during active disease?
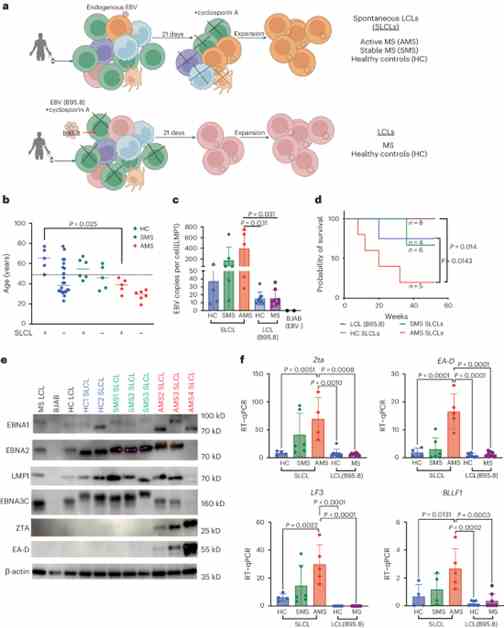
In a comprehensive analysis, researchers found that B cells derived from patients with multiple sclerosis during active disease exhibit distinct gene expression profiles compared to those from healthy controls. These differences highlight the role of EBV and host genes in the development and progression of multiple sclerosis.
The study revealed significant upregulation of EBV latent genes, including EBNA1 and LMP1, as well as lytic genes such as Zta and EA-D in B cells from patients with active multiple sclerosis. This suggests a potential link between EBV infection and the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis.
How do these findings impact our understanding of multiple sclerosis and EBV infection?
These findings provide valuable insights into the complex interplay between EBV infection and host gene expression in the context of multiple sclerosis. By elucidating the distinct gene expression profiles of B cells in patients with active disease, this study opens new avenues for research and potential therapeutic interventions targeting EBV in the treatment of multiple sclerosis.
Overall, this study contributes to a deeper understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying multiple sclerosis and highlights the importance of investigating the role of EBV in autoimmune diseases. The findings pave the way for future studies aimed at developing targeted therapies for multiple sclerosis based on these gene expression profiles.
Tags: multiple sclerosis, B cells, gene expression, EBV, host genes, active disease, autoimmune diseases, therapeutic interventions, molecular mechanisms, research, treatment.