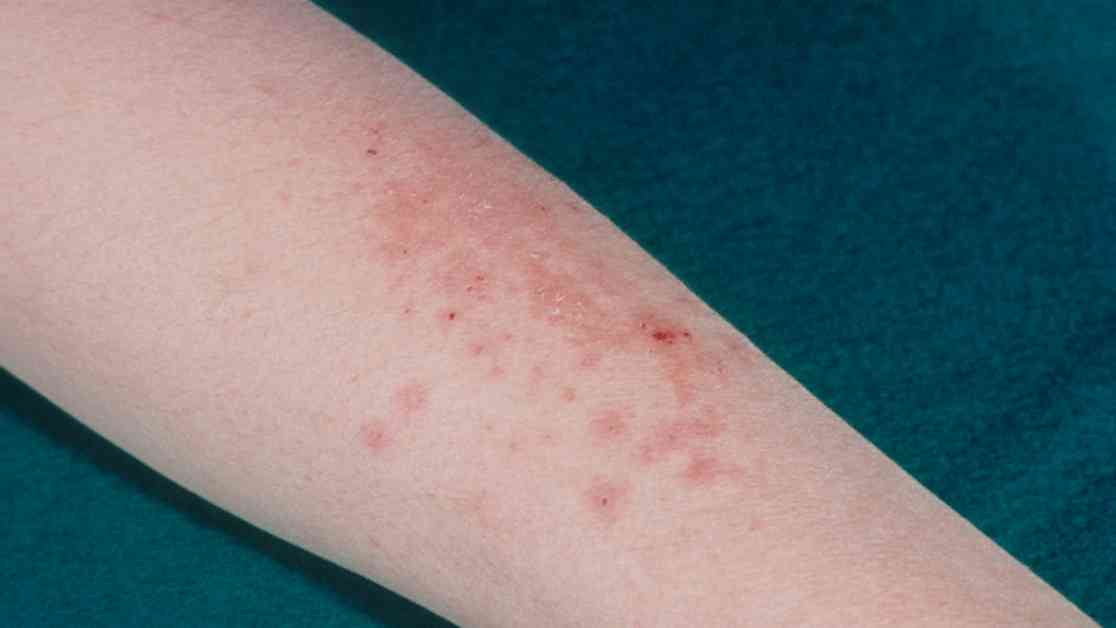
Health officials in New York City are alerting the public about a rare case of ringworm that is believed to have been transmitted through sexual contact. This particular infection is caused by a fungus known as trichophyton mentagrophytes type VII (TMVII) and has been identified in a man in his 30s who engaged in sexual activities with multiple partners during trips to England, Greece, and California.
Upon returning from his travels, the man developed a red, itchy rash on his genital area, legs, groin, and buttocks, which was initially mistaken for eczema due to its appearance. Tests confirmed the presence of the fungus, and the man underwent treatment with antifungal medications for several months before the infection cleared.
Even though this is the first reported case of TMVII in the U.S., similar infections have been documented in other countries, particularly among men who have sex with men. Physicians are urged to inquire about rashes in the genital area, especially in patients who are sexually active and have recently traveled abroad. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent the spread of the infection.
The emergence of this rare form of ringworm highlights the importance of ongoing research and surveillance efforts to track new cases and understand how these fungal infections evolve. Dr. Avrom Caplan, along with his team at NYU Langone Health, is actively studying these cases and collaborating with experts nationally and internationally to enhance our understanding of these infections and improve treatment strategies.
While this particular case of sexually transmitted ringworm in New York City may be rare, it serves as a reminder of the importance of practicing safe sex and seeking medical attention for unusual skin symptoms. By raising awareness and conducting further research, healthcare professionals can better address and manage these infections to safeguard public health.