Brad Marchand, the Boston Bruins captain, suffered a concussion during a playoff game after colliding with an opponent. Despite showing signs of a head injury, Marchand continued to play until the medical staff pulled him out of the game. He later admitted to not being upfront about his condition.
The current concussion evaluation protocol in the NHL relies on subjective observations and symptom reporting by players. These methods are not always accurate and can be influenced by various factors, leading to potential misdiagnoses. Traditional diagnostic tools like the Sport Concussion Assessment Tool (SCAT5) have limitations in detecting concussions.
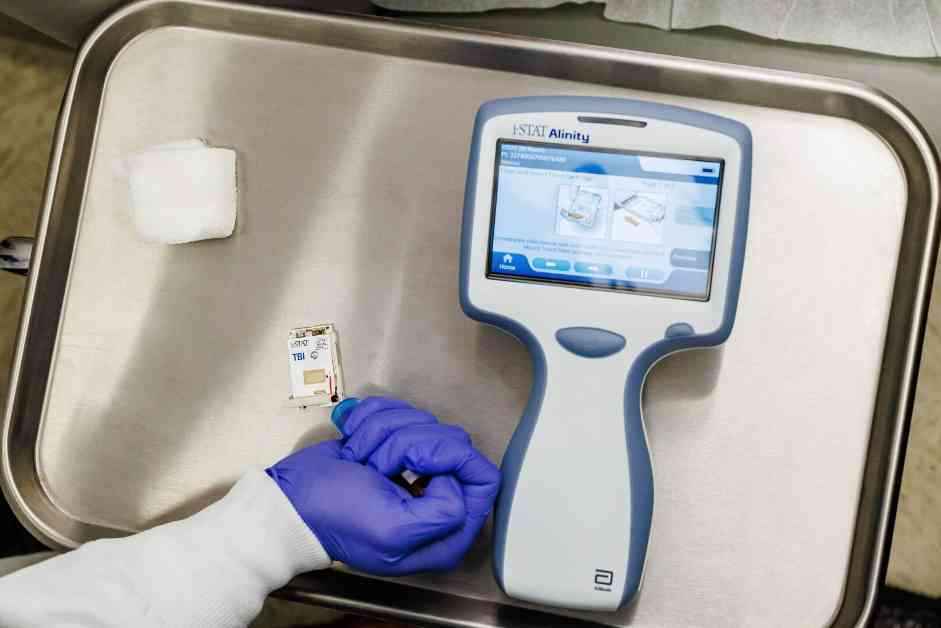
To address these limitations, the FDA recently approved a blood-based rapid concussion test developed by Abbott. This test measures the levels of specific proteins released by the brain into the bloodstream following a head injury. By analyzing these biomarkers, doctors can quickly and accurately diagnose concussions within 15 minutes.
The introduction of a blood-based concussion test could revolutionize the way head injuries are diagnosed in sports, including the NHL. Players who may hide their symptoms or downplay their injuries could benefit from an objective test that provides clear results. This could lead to faster and more effective treatment, reducing the risk of long-term consequences from untreated concussions.
In addition to improving player safety, the blood-based test could also help prevent misdiagnoses and unnecessary removal from play. By providing a more reliable assessment of concussions, teams and players can make informed decisions about returning to the game without compromising their health.
Overall, the approval of the blood-based concussion test represents a significant advancement in sports medicine. It offers a promising solution to the challenges faced by medical professionals in accurately diagnosing head injuries and ensuring the well-being of athletes. By embracing this new technology, the NHL and other sports organizations can prioritize player safety and health in a more efficient and effective manner.